HEAD INJURIES
Head Injuries are:
- Very common in Road Traffic Accidents
- Major Cause of death among youth
- Severity depends on Brain injury
Head Injuries Involve scalp, cranium, or underlying brain
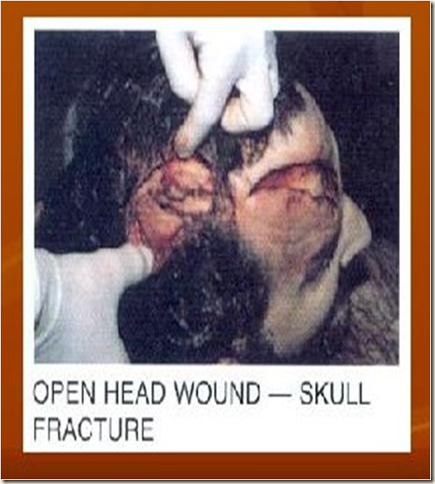
- Scalp -- lacerations, contusions, abrasions
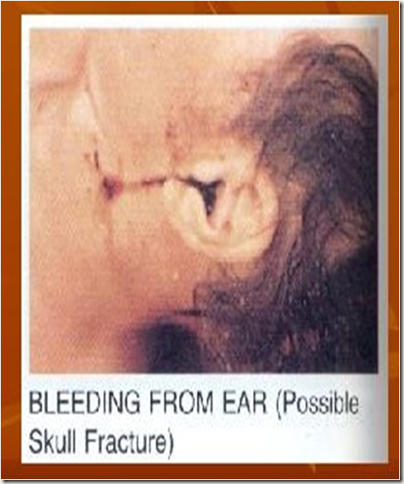
- Skull fractures -- vault / base, simple or compound,
- depressed or planar
- Brain Injury: Focal (intra-cranial haematoma, contusion)
- Diffuse (diffuse axonal injury)
- May be Open or Closed
Types of Head Injuries
- Coup / Counter coup injury
- Concussion
- Cerebral Contusion
- Cerebral Haemotoma or bleed
- Epidural
- Sub-dural
- Sub-arachnoid
- Intra-cerebral
Signs and Symptoms
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea / Vomiting
- Amnesia
- Decreased responsiveness
- Confusion
- Irritability
- Loss of responsiveness
For HEAD INJURY patient :
- First impression: Responsive or Unresponsive
- Urgent Survey ABCDE
- Open airway with C-spine
- Check breathing: Ventilate; Oral airway; O2
- Check carotid artery pulse – CPR if indicated
- Control any major bleeding
INVESTIGATIONS FOR JEAD INJURY PATIENTS:
- CBC
- Blood Urea / Serum Creatinin
- Serum Electrolytes
- Blood Group / Cross Match
- X-Ray Skull
- CT Brain
MANAGEMENT OF HEAD INJURY PATIENTS :
MASK an Ambu bagging if indicated.



DO General Measures in Head Injury Patients
- Stabilize head
- Maintain body temp.
- Observe – seizures, vomiting, change in response
- Presume C-Spine injury – Cervical collar
- Open airway: administer oxygen
- Treat bleeding and shock
- Prevent aspiration of vomit / secretions
- Vital monitoring
Do Specific Measures in Head Injury Patients
- NG tube (Nasogastric tube) is passed in head injury patients the reason being risk of aspiration of gastric contents. By means of NG tube , stomach contents are emptied. Also in an unconscious patient with longterm t/m going on, it may be used for feeding purposes.
- Folley Catheter is passed to monitor urine output in head injury patients
- Manitol if evidence of cerebral edema
- Steroids
- Antibiotics administration for wounds
- Stitching of Scalp wounds if any
Specialized Management for Head Injury if there is hematoma formation , which is compressing brain tissue
Burr – Hole and evacuation of Haematoma



Comments
Post a Comment